Introduction
Nothing to say more than hello 👋, In Case your wondering who is this man in the banner it's the Khwarizmi the inventor of algorithms concept. Make sure to follow because I will start more advanced series in future.
Linked List
Single Linked List
struct node
{
char data;
struct node *next;
}
self reference structures we talk about them before.
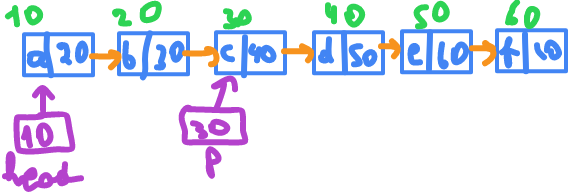
first element is called head.
arrays are dynamic access , while linked lists are sequential accessible , it mean you need to visit all the previous element in order to reach the element you need , it mean
O(n)
while arrays are
O(1)
searching in both will take
O(n)
.
struct node *p;
p = head->next->next; // 30
p->next->next->next=p; // 50 will link to 30 , so 60 is lost
head->next=p->next; // 10 will link to 40
printf("%c" , head->next->next->next->next->data); // d
This linked list is same for all the followings. We are assuming that our linked list have more than 1 node , if it is 1 node we should put conditions to make sure that if our linked list can perform certain things.
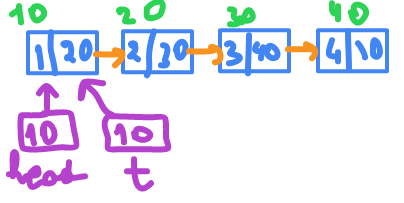
Traversing a single linked list
struct node *t;
t = head;
while(t != NULL) { // or while(t) have same meaning
printf("%d\n" , t->data);
t=t->next;
}
we are using
t
because if we lost the head , it's mean we lost the entire node.
Inserting an element in single linked list
struct node* new = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node))
this is will create a pointer called new
a) insert at beginning :
new->next=head;
head = new;
b) insert at the end
while(t->next != NULL) {
t=t->next;
}
t->next = new;
new->next = NULL;
c) insert a node at specific element
struct node
{
int i;
struct node *next;
}
// asume we need to insert after node 2
while(t->i != 2)
{
t = t->next;
}
new->next = t->next;
t->next = new;
Deleting a node from single linked list
malloc
will create a space for us while
free
will free the memory that we got it from
malloc
// assume we are resetting the linked list to it's init state
// deleting a node from the head
head = head->next;
free(t);
// deleting a node from the tail
while(t->next->next != NULL) {
t = t->next;
}
free(t->next);
t->next=NULL;
// delete a specific node
while(t->next->i != 3){
t = t->next;
}
struct node *t1 = t->next;
t->next = t1->next; // or t->next->next
free(t1);
example 1
struct node
{
int val;
struct node *next;
};
void rearrange(struct node *list)
{
struct node *p , *q;
int temp;
if(!list || !list->next) return; // if linkedlist have no or 1 element return
p = list; q=list->next; // q pointing to 1st element and q to second
while(q) // while q is not null do
{
temp = p->val;p->val=q->val;
q->val=temp;p=q->next; // swap q and p
q=p?p->next:0; // if p is pointing to something it will take it otherwise 0
}
}
// output : 2 1 4 3 6 5 7
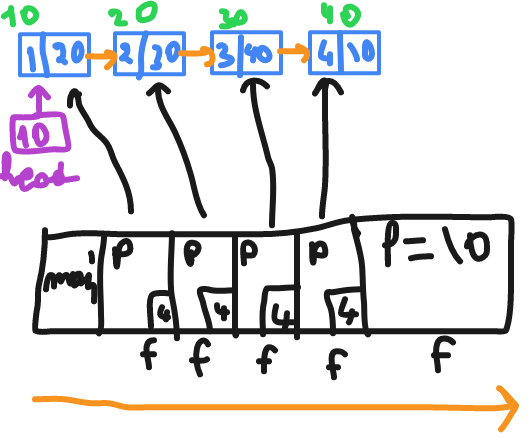
printing the elements using recursion
// print then recursion
void f(struct node *p)
{
if(p)//1
{//2
printf("%d" , p->data);//3
f(p->link);//4
}//5
}
// output : 1 2 3 4
It will print before start go into next stack
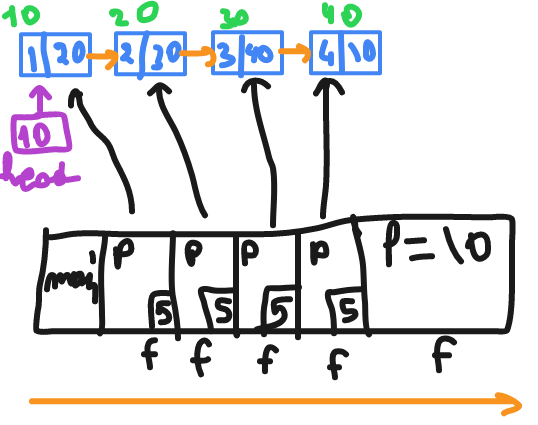
when it's go back it will return to line 5
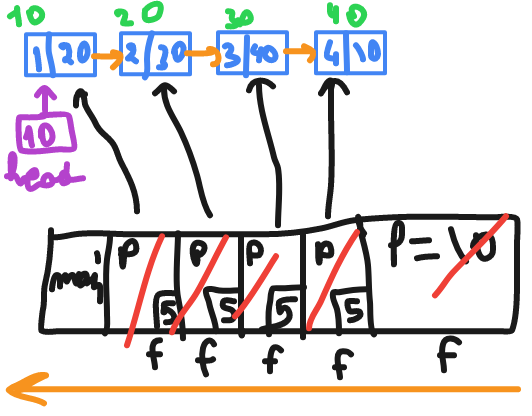
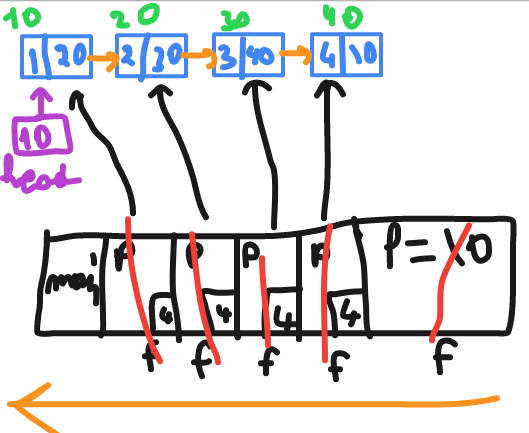
// recursion then print === print in reverse order
void f(struct node *p)
{
if(p)//1
{//2
f(p->link);//3
printf("$d" , p->data);//4
}//5
}
// output : 4 3 2 1
then when it go back it will start at line 4 which printing the value of p stored inside of each stack
Reversing an single linked list using iteration
struct node
{
int i;
struct node * next;
}
struct node * reverse(struct node * cur)
{
struct node *prev = NULL,*nextNode = NULL;
while(cur)
{
nextNode = cur->next;
cur->next=prev;
prev=cur;
cur=nextNode;
}
return prev;
}
Reversing an single linked list using recursion
struct node *head;
void reverse(struct node *prev , struct node *cur)
{
if(cur)
{
reverse(cur , cur->next);
cur->next = prev;
} else
head = prev;
}
void main()
{
//...
reverse(NULL , head);
//..
}
circular Linked List
circular linked list have it's tail pointing to sentinel which is the head but containing the number of nodes instead with pointer to first element.
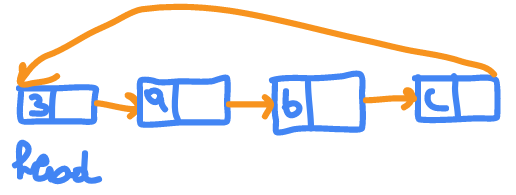
while(p->next != head){}
double linked list

// insert at start
struct node {
int i;
struct node *prev;
struct node *next;
};
t->next = head;
head = t;
t->prev = NULL;
head->next->prev = head;
// insert at the end
while(p->next) p = p->next;
p->next=t;
t->prev=p;
t->next=NULL;
// insert between > 1 and < n where n is number of node
t->prev=p; // p is the pointer of the element previous to t
t->next=p->next;
p->next=t;
t->next->prev=t;